What is DeFi
Decentralized finance, or DeFi, refers to a new financial system built on blockchain technology, indeed.
Moreover, peer-to-peer decentralized financial applications that are not controlled by any single entity.
Then, self-executing smart contracts is base for DeFi applications.
Especially, the terms of the contract between the buyer and the seller are written directly in the lines of code.
So to say, smart contracts allow you to automate financial transactions, making them fast, efficient, and secure.
How Does DeFi Work?
Decentralized finance, or “DeFi” for short, is a new financial system built on blockchain technology such as Ethereum. Here is an example of how satoshis works:
a) The user creates a new Ethereum wallet and adds some Ether (ETH) to it,
b) The user then uses his wallet to interact with a DeFi application such as a lending platform,
c) The lending platform allows the user to borrow another cryptocurrency such as DAI using ETH as collateral,
d) The user can now use the borrowed DAI to invest in other DeFi applications such as a prediction market or crop farming platform,
e) surely, you get a return on your investment which you can use to repay the loan and make a profit.
Especially, the lending platform uses smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain to automatically manage the loan and ensure that the user’s collateral is always sufficient to cover the loan.
Because the sats application is built on the blockchain, it operates in a trustless and decentralized manner, allowing users to interact with the platform without intermediaries such as banks.
It’s worth noting that since the DeFi ecosystem is constantly evolving, the example is just a way to understand the basics, and the specific platform you’re using may have a different mechanism.
Either way, sats opens up new trading opportunities with cryptocurrencies.

Make money with DeFi isn’t so much difficult as like you see.
Benefits of DeFi
One of the key advantages of DeFi is that it enables greater availability of financial services.
Traditional financial systems often have strict requirements for access to services, such as minimum account balances or good credit scores.
So with DeFi, anyone with an internet connection can access a wide range of financial services,
including borrowing, lending, and trading.
Another important advantage of DeFi is the ability to create new forms of financial instruments.
For example, decentralized exchanges (DEX) allow digital assets to be traded in a decentralized and trustless manner.
Without a doubt, decentralized lending platforms allow individuals
to borrow and borrow money without the need for a centralized intermediary.
What’s more, decentralized insurance platforms allow individuals to purchase insurance policies
without having to rely on traditional insurance companies.
Surely, DeFi brings benefits to the table and that’s why people use it.
Disadvantages of DeFi
Due to the young DeFi sector, there are also disadvantages to using this cryptocurrency sector.
Complexity
Firstly, sats projects are often complex and require a high level of technical knowledge to navigate, which can be a barrier for many users.
Volatility
Secondly, the value of DeFi assets can be very volatile, making them a risky investment for many people,
Lack of Regulation
Following, many satoshis projects operate in a regulatory gray area, which can create uncertainty and risk for investors,
Risks of Smart Contracts
Last, but not at least, smart contracts are prone to bugs and hacks that can lead to users losing their funds,
Limited Adoption
Despite the growing popularity of DeFi, the sector still has limited mainstream adoption and acceptance, which can make it difficult for users to find liquidity and access the full range of DeFi services.
Due to the young sector, too much trust in sats platforms can end disastrously. If we add that the cryptocurrency sector itself is very modern and is just being born. The question marks themselves appear without a moment’s thought, indeed.
As well as that, DeFi applications have advantage, they have disadvantage as well.
New Sources of Revenue
Decentralized Finance is also helping to create new forms of revenue streams. Therefore, yield farming is an example of a new revenue stream that has emerged in the satoshis space. Particularly, yield farming refers to the practice of lending or rolling digital assets to earn interest or rewards. This allows individuals to get a return on their digital assets without having to sell them.
DeFi Ecosystem
The DeFi ecosystem is still in its early stages but is growing rapidly. The total value locked in Decetralized Finance protocols has grown from around $1 billion in 2019 to over $20 billion in 2021. This growth was due to the growing number of decentralized applications built on blockchain technology, as well as the growing interest in digital technology assets.
However, DeFi is not without its challenges. One of the biggest challenges is scalability. As the number of users and transactions on DeFi platforms increases, the networks they operate on may struggle to keep up. Additionally, there is a lack of regulatory clarity around sats, which could lead to potential legal issues in the future.
The most important projects of the Decentralized Finance ecosystem are: Lido Stake Ether (STETH), DAI (DAI), Uniswap (UNI), Chainlink (LINK), Lido DAO (LDO), Terra Luna Classic (LUNC), Frax (FRAX), Aave (AAVE), Maker (MKR), PancakeSwap (CAKE).
For more information, see the DeFi ecosystem
Holy Grail of DeFi – Ethereum
DeFi, or decentralized finance, is a movement that aims to use blockchain technology and smart contracts to create financial products and services that are open and accessible to everyone, without the need for intermediaries such as banks.
Ethereum is the second largest blockchain network by market capitalization. People name it the “holy grail” of DeFi due to the large and active developer community that has built a wide range of DeFi applications on the Ethereum network. These applications include decentralized exchanges (DEX), borrowing and lending platforms, stablecoins, and much more.
Ethereum’s smart contract functionality allows for the creation of incredible, transparent, and highly customizable financial products. Ethereum is a key player in the decentralized financial ecosystem.
Decentralized Vs Traditional Finance
Decentralized finance (DeFi) refers to financial systems built on blockchain technology that operates without the need for a central authority or intermediary. Transactions are made directly between users and smart contracts and decentralized protocols rule the system.
Centrally managed finance, on the other hand, refers to traditional financial systems. Banks and financial institutions making all the transactions. Central authority control whole system and make regulations.
The main difference between the two is how they operate. DeFi is decentralized and operate on a peer-to-peer basis. In centrally managed finance central authority control whole system.
Sats offers greater transparency and accessibility, as well as the ability to operate 24/7. In centraly managed finance there are hours of operation.
Satoshis Risks
Some potential DeFi risks include.
Smart Contract Risks
Because DeFi is based on blockchain technology, it relies heavily on smart contracts. These are self-executing contracts where the terms of the contract between the buyer and the seller are written directly into lines of code. However, if there is a bug in the code or an exploit is found, you may lose your funds.
Liquidity Risks
Many DeFi projects have low trading volume and liquidity, which can make it difficult to buy or sell assets. This can lead to large spreads between the bid and ask prices, making it difficult for investors to trade at a fair price.
Volatility Risks
DeFi projects are often very volatile, which can lead to large losses if the value of the asset drops quickly.
Regulatory Risks
The DeFi regulatory environment remains uncertain, which could lead to project closures or legal challenges.
Counterparty Risks
DeFi projects are often built on top of other blockchain projects such as Ethereum. If the underlying blockchain runs into problems, DeFi projects built on top of it could be negatively impacted.
Storage Risks
DeFi projects often require users to deposit their assets into a smart contract, which can be vulnerable to hacking and theft.
The Present of Decentralized Finance
To determine the interest in DeFi, I will use charts taken from Google Trends.
This is only an approximation. Be that as it may, Google is the most popular search engine on the Internet and is often a good indicator of interest in the topic you are looking for.
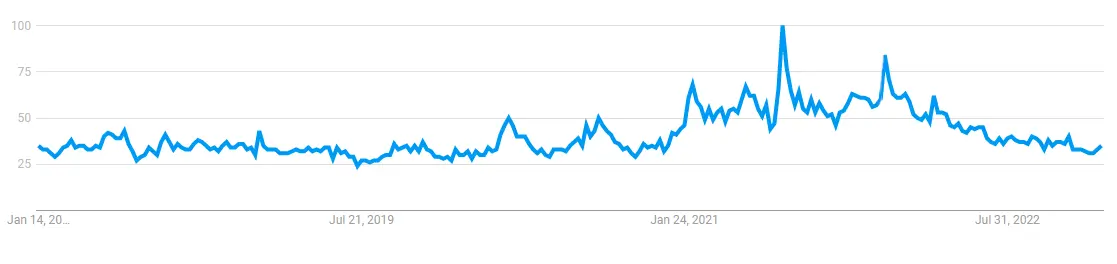
Interest in DeFi decreases during the bear market and increases during the bull market. This is quite logical because a bear market is a period of less interest in cryptocurrencies and all kinds of high-risk assets.
During the period of the end of the bear market or the beginning of the bull market (you have to wait a few months to verify this)
the level of interest in DeFi is around 32-35. Let’s look at the Fear and Greed index to assess more closely whether the bear market is over (once again, it’s just a graph that is only an approximation of investors’ sentiment).
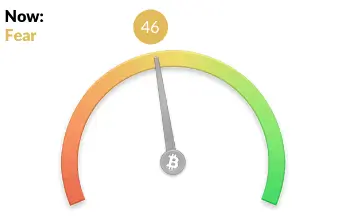
Fear, rating: 46, which means that sentiments are changing. The bear market is over. Regarding DeFi I have following conclusion: The chart returned to the previous cycle from July 2019, i.e. interest will grow in the coming months. The same conclusion is for the entire cryptocurrency market.
The improving macroeconomic situation, and at the same time the falling CPI index, additionally works in favor of the return of the bull market.
Future of Decentralized Finance
With the development of decentralized banking and the adoption of cryptocurrencies, there will be a large number of new projects related to DeFi. It seems that Ethereum will remain number one in terms of projects based on blockchain.
In addition, there will be even more automation in the DeFi area. The effect of this can be shopping without human involvement. It sounds quite abstract, but machines will be able to communicate with each other using Artificial Intelligence and will make purchases themselves, learning about our preferences.
The missing link in this case is digital currencies, and these are becoming more and more common thanks to decentralized finance.
We are currently in the age of Internet-of-Things, but the next step will be Economy-of-Things based on AI and blockchain.
Going even further, we can witness self-managed decentralized banking exchanges.
It sounds really scary, but … At the moment when AI starts to manage stock exchanges, assumptions will become a fact.
Conclusions
In summary, DeFi is a new blockchain-based financial system that is changing the way financial services are delivered.
It allows greater access to financial services,
the creation of new financial instruments, and new streams of income.
While the DeFi ecosystem is still in its early stages,
it is growing rapidly and has the potential to revolutionize the financial industry.
However, scalability and regulatory challenges will need to be addressed for DeFi to reach its full potential.

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.