Introduction
Indeed, cryptography, the underpinning technology of cryptocurrencies, has been the foundation of secure communication throughout centuries.
From ancient cipher systems to modern encryption methods, cryptography continues to evolve, because providing secure channels of communication and data protection.
Today, it forms the backbone of cryptocurrencies, instilling trust in a decentralized and digital financial system, in fact.
In this article little bit more about cryptography in cryptocurrencies, because they are interesting us on this website.
Understanding Cryptography

Cryptography, derived from the Greek words “kryptós” (hidden) and “graphein” (to write), in fact. Above all, is the science of encoding and decoding information.
Its primary aim is to ensure confidentiality, integrity, and also authenticity of data. In the context of cryptocurrencies, cryptography is leveraged to secure transactions, but also control new unit creation, and verify transfer of digital assets.
Crypto as Concealed Aspect of Cryptocurrencies
Obviously, the term ‘crypto’ in ‘cryptocurrency’ is a reference to the cryptographic techniques employed.
Furthermore, cryptography ensures that users can trust the system without necessarily trusting each other or a central authority. The cryptographic principles make it possible to create proof of digital events, like transactions, and then store them in a public ledger known as blockchain.
From Conventional Money To Cryptocurrencies
Traditional fiat currencies, such as the US Dollar or Euro, are issued and regulated by central banks. The value of these currencies relies on the economic power and stability of respective countries.
Conversely, cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin are decentralized and operate on pre-determined, computer-controlled monetary policies.
Instead of placing trust in governments or financial institutions, cryptocurrency users place trust in the underlying cryptography and the transparent set of governing rules.
Cryptography In Cryptocurrencies
Cryptocurrencies employ two primary cryptographic techniques: one for generating public-private key pairs, and another for validating transactions.
The public-private key pairs are used to create crypto wallet addresses and sign transactions, while a hash function validates the integrity of transactions and maintains the structure of the blockchain.
Symmetric vs Asymmetric Cryptography
Cryptography can be categorized into two types: symmetric and asymmetric.
Symmetric Cryptography
In symmetric cryptography, the same key is used for both encryption and decryption. It’s simpler and faster than asymmetric cryptography but can pose a challenge when it comes to key exchange between communicating parties.
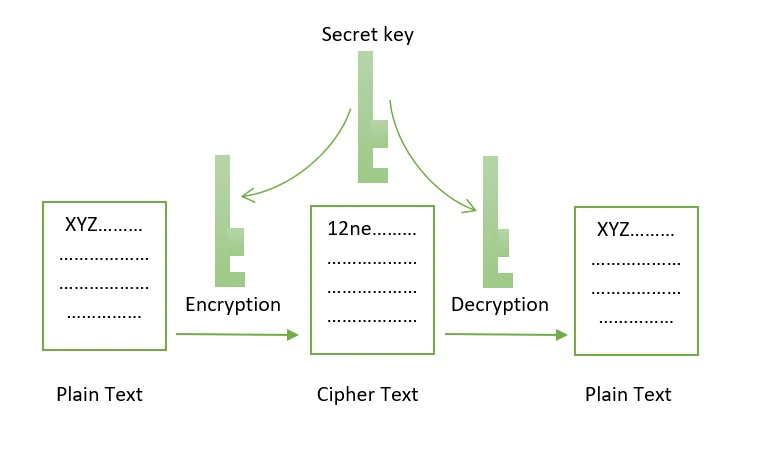
Indeed, in symmetric encryption, the same key is used to encrypt and decrypt the message.
In communication, this means that the same key is used by the recipient and the sender of the message.
From a security point of view, this means that the intercepted key allows messages to be encrypted in unauthorized hands.
Asymmetric Cryptography
Asymmetric cryptography, also known as public-key cryptography, uses two distinct keys for encryption and decryption.
The public key is accessible to everyone, while the private key remains secret to the owner.
Most cryptocurrencies use the public-private key pairs created by asymmetric cryptographic methods.
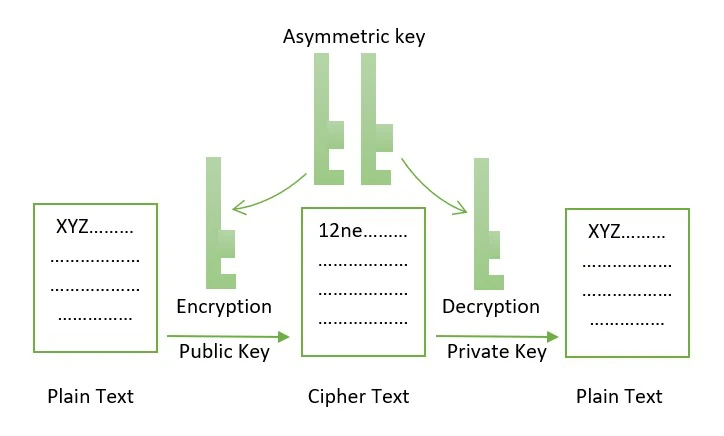
In contrast, an asymmetric key uses a private and public key.
The public key encrypts the message, but only the private key decrypts it. That’s why keeping your private key safe is so important.
A person who knows the private key has access to the decrypted message. The public key is officially available to everyone.
Hash Functions
Hash functions, a critical component of cryptography, convert an input (or ‘message’) into a fixed string of digits, typically a hash value (or ‘digest’).
This transformation is deterministic, meaning the same input will always produce the same hash value. Hash functions are essential for efficiently verifying the integrity of transactions on the network and maintaining the structure of the blockchain.
What is Bitcoin Hashrate?
Bitcoin hashrate is a metric connected to the process of Bitcoin mining.
Bitcoin mining is the process of solving complex mathematical puzzles to be rewarded with bitcoin. The process of Bitcoin mining secures the network and also confirms that transactions on the blockchain are correct.
Mining hash rate is therefore a key security metric for Bitcoin. That is because the greater the levels of hashing power (can be thought of as computing power) that is operating on the network, the harder it would be for someone to overpower and attack the network.
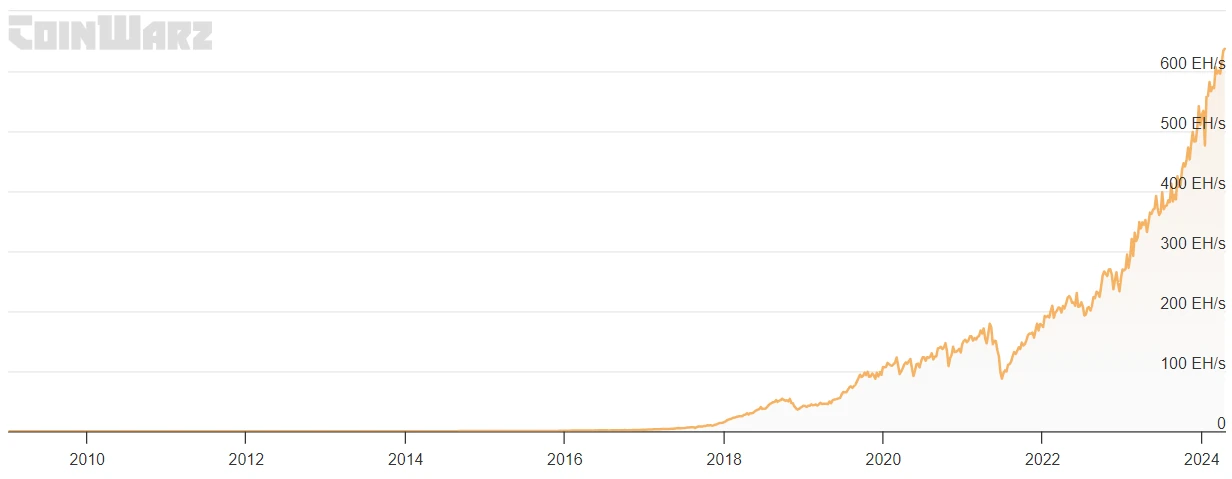
The security of the Bitcoin network increases every year.
If hashrate on the Bitcoin network is high then this indicates that the network is secure and healthy. This is reassuring to investors who would not want to invest in a network that is not secure.
Cryptography and The Trustless Operation
One of the most significant advantages of cryptographic systems is their ability to operate trustlessly.
By decentralizing control and eliminating human involvement, transactions can be processed faster, and fees are often cheaper than traditional banking solutions.
Cryptographic Efficiency in Crypto
Knowing the effectiveness of using cryptography in various situations is important.
Because the best solutions are selected when the needs of cryptography are met while maintaining the effectiveness and speed of communication.
The graphic taken from Crypto.com perfectly illustrates where the hash function, symmetric and asymmetric key can be used.
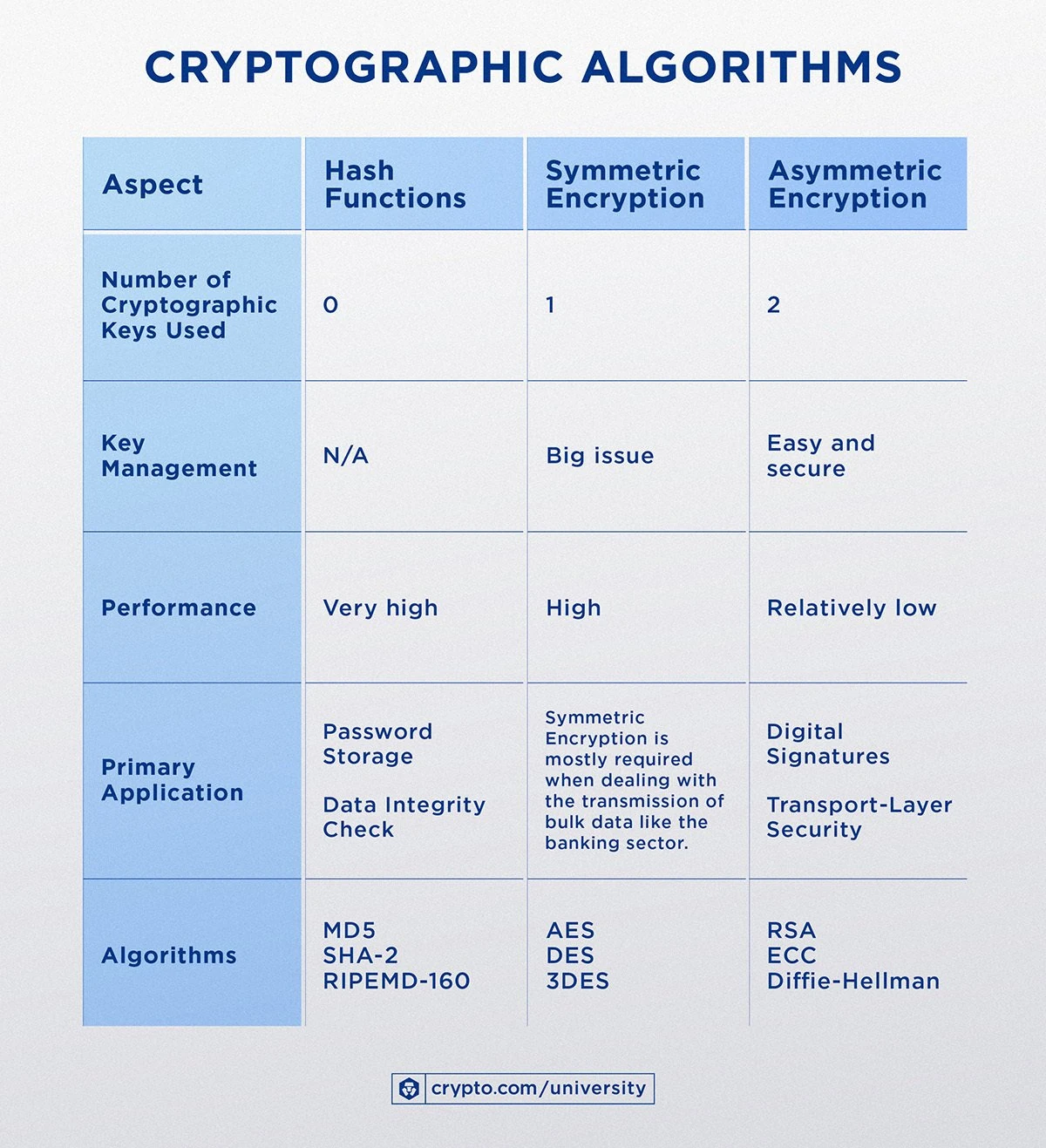
Without a doubt, the choice of cryptographic algorithm is appropriate for the application.
As I mentioned earlier, choosing the right solution is adequate to the need. Hash functions are used to store data.
Symmetric cryptography in banking transactions, and asymmetric solutions in digital signatures and encrypted connections between two communication channels.
Popular Cryptographic Techniques
Various cryptographic techniques have been adopted in cryptocurrencies, including RSA, Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC), and Secure Hash Algorithm 256 (SHA-256), DES and AES.
RSA
Firstly, RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman) is an asymmetric cryptographic algorithm widely used in cryptocurrencies. It enables users to create a public-private key pair, with the public key used to encrypt a message, and the private key used to decrypt it.
Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC)
Second, ECC is another asymmetric cryptographic algorithm utilized in cryptocurrencies.
It provides a higher level of security with shorter keys, making it more efficient. Bitcoin, for instance, uses a specific ECC method known as secp256k1 for generating public-private key pairs.
Secure Hash Algorithm 256 (SHA-256)
Thirdly, SHA-256 is a member of the Secure Hash Algorithm family.
It generates an almost-unique, fixed-size 256-bit hash of a given input. Moreover, Bitcoin uses SHA-256 for encrypting data stored in blocks, validating transactions, and maintaining the structure of the blockchain.
DES
Generally, it is a symmetric algorithm and the DES algorithm uses a key of 56-bit size. Additionally, using this key, the DES takes a block of 64-bit plain text as input and generates a block of 64-bit cipher text.
AES
The AES Encryption algorithm (also known as the Rijndael algorithm) is a symmetric block cipher algorithm with a block/chunk size of 128 bits.
Indeed, it converts these individual blocks using keys of 128, 192, and 256 bits.
Once it encrypts these blocks, it joins them together to form the ciphertext.
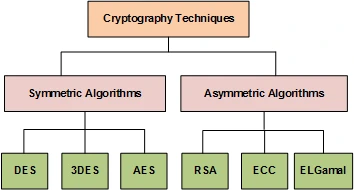
In fact, the main division in cryptographic techniques is symmetric and asymmetric algorithms.
I have already explained that they differ in the number of keys used, as well as in performance and where they are used.
The most important thing is that you remember the division into two categories and that Bitcon uses asymmetric algorithms.
Cryptography as and Crypto Security
Cryptography plays a vital role in securing cryptocurrency networks against cyber attacks.
The total computational power dedicated to mining cryptocurrencies, known as a network’s hash rate, helps secure the network against potential threats.
An attack such as a 51% attack, where an entity gains control of the majority of the network’s hash rate, becomes computationally difficult, thus safeguarding the integrity of the network.
Cryptography and Bitcoin Mining
Bitcoin, the pioneer of cryptocurrencies, employs a process known as mining to issue new units of currency.
Mining is part of the proof-of-work consensus mechanism that enables honest participants to add new blocks of data to the blockchain. This process involves the use of hash functions, making cryptography a vital part of the process.
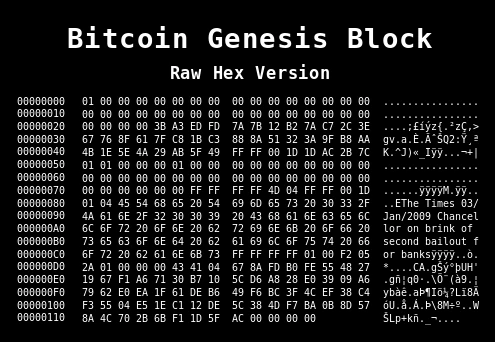
A genesis block is the first block of a block chain.
Modern versions of Bitcoin number it as block 0, though very early versions counted it as block 1.
The genesis block is almost always hardcoded into the software of the applications that utilize its block chain, also. It is a special case in that it does not reference a previous block, and for Bitcoin and almost all of its derivatives, it produces an unspendable subsidy.
Bitcoin Halving
Since the fourth Bitcoin halving took place tonight, it’s time to mention what it means for the cryptocurrency market.
Well, what does this really mean?
Well, every halving, Bitcoin miners receive smaller rewards for mining the cryptocurrency.
The rewards are, of course, in the form of the cryptocurrency itself.
At the same time, there is a decline in bitcoin’s inflation rate according to the cryptocurrency’s monetary policy.
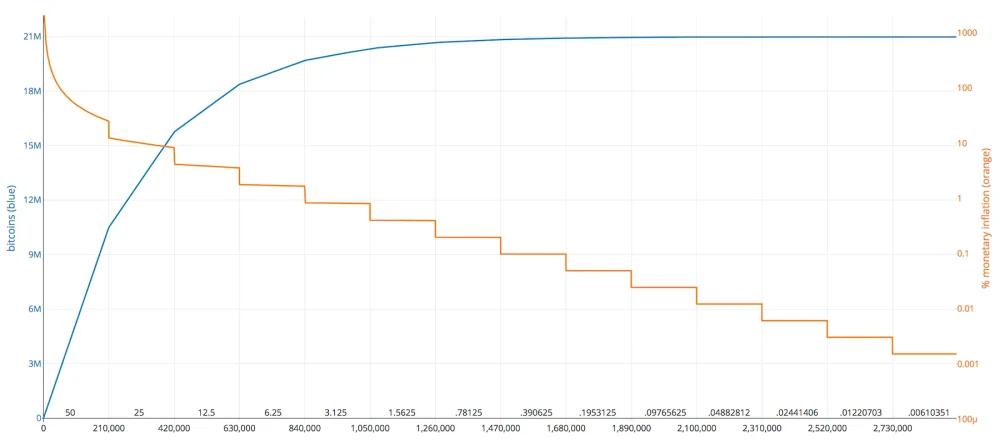
You can easily read from the chart that Bitcoin now has an inflation rate of 1%!
In addition to this, there are only 4 bitcoin halvings behind us.
The situation is becoming more and more interesting as a matter of fact. Moreover, you can read more about halving here.
Digital Signatures and Cryptography
Digital signatures are a crucial aspect of cryptocurrencies, allowing senders to prove they own the corresponding private key to a specific public key without revealing their private key.
Besides, Bitcoin uses the Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm (ECDSA) to cryptographically approve and send transactions from a crypto wallet.
Conclusions
Without doubt cryptography is integral to the functionality and security of cryptocurrencies.
It is the linchpin that holds the entire system together, enabling secure, trustless transactions as well.
In general, providing an irrefutable means of proving ownership of funds.
Cryptography is an inherent element of cryptocurrencies, surely.
It is the use of advanced cryptographic techniques in projects like Bitcoin that makes them so secure.

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.