Introduction to CBDC
In fact, today’s ever-evolving digital world, financial systems are constantly being redefined to adapt to the changing needs of individuals and businesses. One such innovation that has gained significant traction in recent years is Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) all around the world, in general.
CBDC, also known as digital fiat currency, is a form of digital currency that is issued by a central bank and represents a sovereign nation’s official currency.
Unlike cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, CBDC is centralized and regulated by a central authority, making it a more viable option for widespread adoption and integration into existing financial systems.
Today article is exactly about CBDC and some secrets what I present right now.
Meaning of CBDC
At first, CBDC, as the name suggests, is a digital representation of a country’s fiat currency.
It is created, issued, and regulated by the central bank of a nation, so that making it a legal tender just like physical cash.
CBDC can be used for various financial transactions, including payments, remittances, and settlements. It is designed to be secure, efficient, and easily accessible to individuals and businesses.

Indeed, CBDCs are intended to play similar roles to cryptocurrencies, but…
There are some very significant differences. I will mention these later in the article.
Evolution of Digital Currencies

The concept of digital currencies is not new. It has been evolving since the advent of the internet. Initially, digital currencies were created and used by private entities as a means of exchange within their closed ecosystems.
However, with the rise of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, the potential for digital currencies to revolutionize the financial landscape became evident.
Cryptocurrencies introduced the concept of decentralized digital currencies, which operate on blockchain technology and are not controlled by any central authority.
While cryptocurrencies have gained popularity, they face challenges such as price volatility and regulatory concerns. This led to the exploration of CBDC as a more stable and regulated alternative.
How does a CBDC Work?
Governments are interested in the improvements blockchain ledgers provide in transferring value, but in a permissioned, rather than permissionless way.
Moreover, CBDC itself can be used in 3 ways.
Without intermediaries, using intermediaries and in a mixed model.
The graphic below perfectly summarizes each of these solutions.

The first scenario, i.e. the one eliminating intermediaries in transactions between the central bank and customers, seems the most likely.
It may also turn out that the role of intermediaries will be limited to a minimum.
The hybrid solution makes the least sense.
Why intermediaries when you can have full control over transactions in your own bank. Makes sense, don’t you think?
Another argument for the decline in the role of intermediaries is the decreasing number of commercial banks in the world.
In this case, I used the example of the USA. The current number of banks in 2024 is close to 2000, based on data from Statista.
The Role of Central Banks
Central banks play a crucial role in the financial landscape of any nation. They are responsible for formulating monetary policy, maintaining price stability, and ensuring the stability of the financial system.
Traditionally, central banks have issued and regulated physical cash, but with the rise of digital transactions, the need for a digital form of currency became apparent.
CBDC allows central banks to maintain control over the monetary system while embracing the benefits of digital currencies.
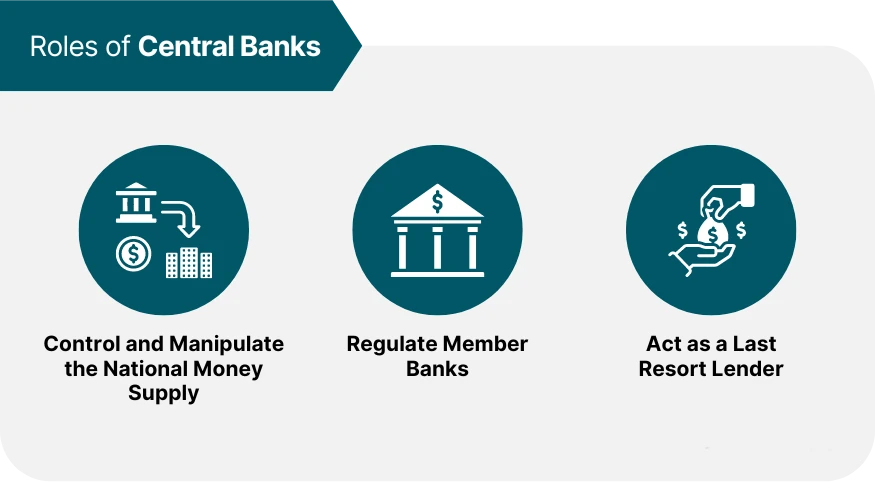
Certainly, the main roles of central banks are to control and manipulate the money supply.
To the obvious benefit of the elites and to the detriment of society.
Another role is regulatory roles. Here you can support each other whether there are more benefits or disadvantages for society.
However, it is true that it is good to operate in a regulated market. This helps avoid many of the frauds that occur in unregulated markets.
We are also talking about cryptocurrencies.
Central banks lend money to commercial banks and thus also regulate the money supply.
Commercial banks, as we know, provide loans to their customers. They create digital currency in banking systems, but maybe more about that another time.
Benefits of CBDC
CBDC offers several benefits that can potentially transform the global financial landscape.
Firstly, it provides a secure and efficient means of conducting financial transactions.
With CBDC, transactions can be completed instantly, eliminating the need for intermediaries and reducing transaction costs.
Secondly, CBDC can enhance financial inclusion by providing access to banking services for the unbanked population. As CBDC can be accessed through digital wallets on smartphones, individuals without access to traditional banking services can participate in the formal economy.
Lastly, CBDC can improve the effectiveness of monetary policy, as central banks can have real-time visibility into transactions and economic activities, enabling them to make informed decisions.
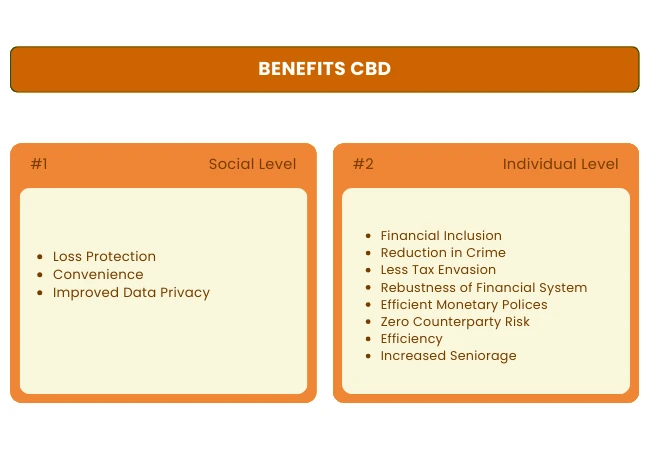
Indeed, some of the benefits of using CBDCs around the world are convincing, but not so soon.
Before we find out about the advantages, it is also worth knowing the disadvantages of CBDCs in the world.
More on these in a moment. For now, I will return to the advantages.
At the individual level, it is a reduction in criminality, probably a more effective monetary policy, an increase in efficiency and an increase in life expectancy.
This is actually what it looks like from an individual’s perspective.
In terms of social benefits, there are convenience, increased data privacy and loss protection.
Are these such good changes?
Potential Risks of CBDC
While the potential benefits of CBDC are significant, there are also challenges and risks that need to be considered.
One of the key challenges is striking the right balance between privacy and transparency. CBDC transactions can be traced, raising concerns about individual privacy.
Additionally, the implementation of CBDC requires robust infrastructure and cybersecurity measures to ensure the system’s integrity and protect against hacking and fraud.
Furthermore, the introduction of CBDC may disrupt existing financial systems and could have unintended consequences on commercial banks and other financial intermediaries.
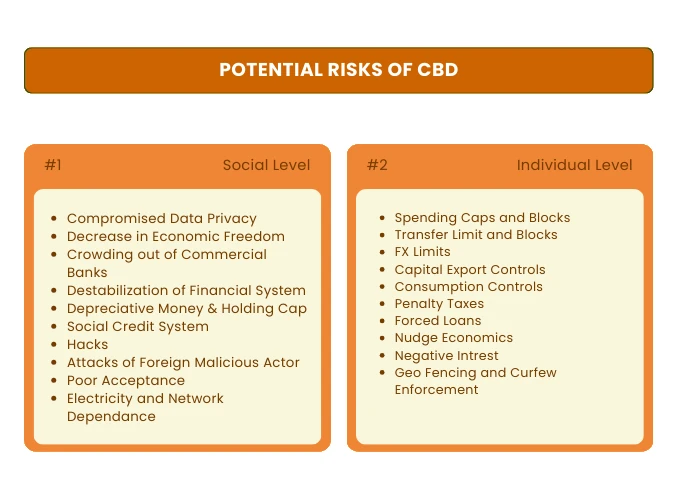
Next, it’s time to find out what the risks associated with CBDC are, and there are many of them. Only after reading this part is it worth forming your opinion about CBDCs and their use.
Here I go.
From an individual point of view, it is full-fledged financial control, imposed taxes and no retention of assets.
Which, in turn, means difficulties in getting rich. How to get rich without savings? Exactly.
But that’s not all. What about controlling your consumption or controlling your spending? Yes, you read that right. CBDC is control in full swing. Okay, what about the social aspects, of which there are also many.
I will just mention a few points.
Lack of economic freedom, social credit system, or destabilization of the financial system. This sounds like a joke, but it isn’t!
Moreover, these are just some of the risks of CBDC for us and society. So now what do you say about CBDC?
CBDC vs Bitcoin
CBDC and cryptocurrencies are often compared, but they are fundamentally different. Bitcoin is decentralized and operate independently of any central authority.
They rely on blockchain technology to validate and record transactions.
On the other hand, CBDC is centralized and regulated by a central bank.
CBDCs are designed to work within existing financial systems, providing stability, regulatory oversight, and legal status.
While bitcoin offer anonymity and freedom from traditional financial institutions, they also face challenges such as price volatility and regulatory concerns.
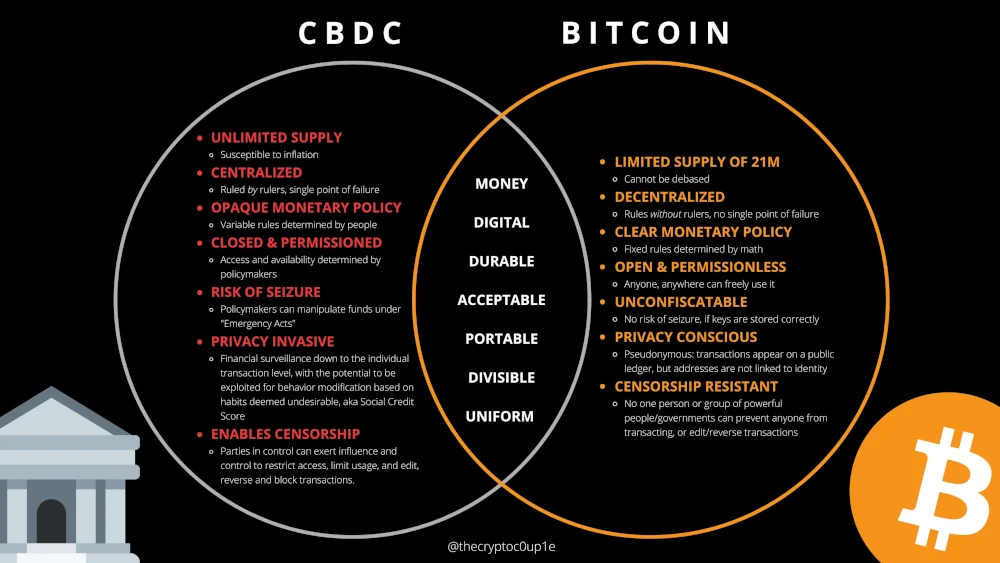
First of all, CBDC is an unlimited supply of money.
At first glance, it may seem quite beneficial, but… constant reprinting by those in power leads to disastrous consequences for society.
Prices of products and goods are in a price bubble.
Therefore, a limited supply like Bitcoin is more healthy. This is a fact that cannot be disputed.
Moreover, limited supply does not give unlimited power to the institutions that manage the supply. Read to central banks.
Another fact is the open policy and access for everyone. When in the case of CBDC, we are talking about access only for those who set the rules.
What about privacy?
The premise of bitcoin is anonymity. It is true that due to pressure from governments, cryptocurrency exchanges had to partially abandon this requirement, but partial anonymity is still possible.
The last point is censorship, which is part of society’s freedom.
Thanks to CBDC, censorship of spoken words takes on a completely different meaning…
Bitcoin is on the side of freedom once again.
CBDC on the World
Countries around the world have recognized the potential of CBDC and have initiated various pilot projects and research initiatives.
China, for example, has made significant progress in developing its digital currency, the Digital Yuan.
The European Central Bank is exploring the possibility of launching a digital euro, while other countries like Sweden and the Bahamas have already conducted pilot projects.
These initiatives aim to understand the feasibility and implications of CBDC on different aspects of the economy, including monetary policy, financial stability, and consumer behavior.
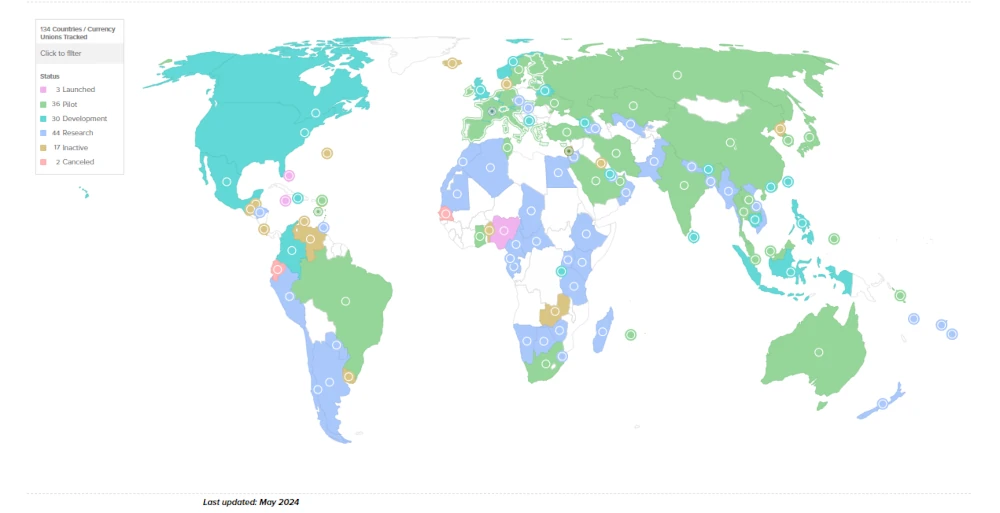
There is no doubt that work on CBDCs is progressing around the world.
It may not be much talked about in the media, but there are currently 135 projects in the world.
The ongoing east-west battle on this issue appears to be somewhat in favor of the east.
In English countries, only Australia and South Africa have a CBDC pilot…
Meanwhile, in the BRICS countries, the pilot is almost everywhere.
Additionally, it must be recognized that the Anglo-Saxons and Europe are working on projects of their own CBDCs.
Implementing CBDC

Implementing CBDC requires careful planning and consideration.
Central banks need to assess the technological requirements, regulatory framework, and potential impact on the financial ecosystem.
The infrastructure for CBDC, including digital wallets, payment systems, and cybersecurity measures, needs to be developed and tested. Additionally, collaboration between central banks, governments, and private sector stakeholders is crucial to ensure a smooth transition and widespread adoption of CBDC.
The Future of CBDC

The future of CBDC holds immense potential for reshaping the global economy. As more countries explore the implementation of CBDC, it is expected to streamline cross-border transactions, simplify international remittances, and reduce dependence on traditional banking systems. CBDC has the potential to enhance financial stability, promote financial inclusion, and drive economic growth.
However, its success will depend on addressing the challenges and risks associated with its implementation and striking the right balance between innovation and regulation.
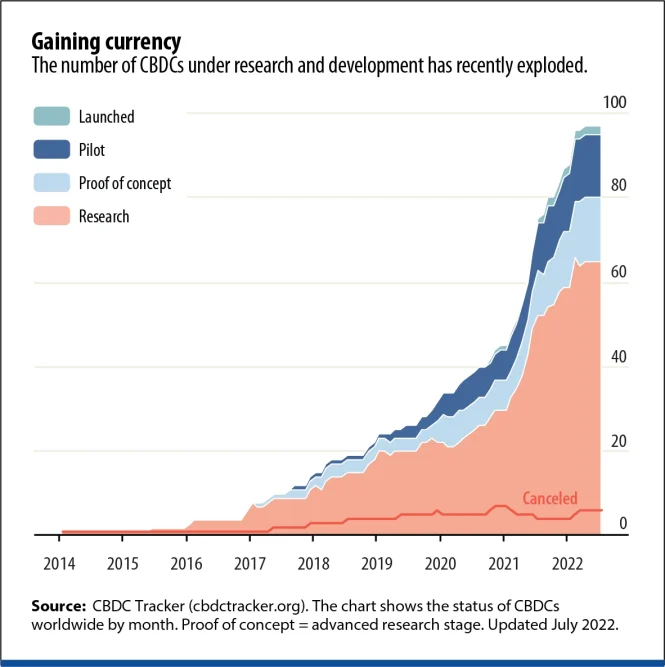
It looks like the future will be dominated by CBDCs. Maybe not necessarily?
However, the data shows one thing – intensive work on CBDCs is underway around the world.
For comparison, I am also posting two graphics showing how much has changed over the last 3 years.
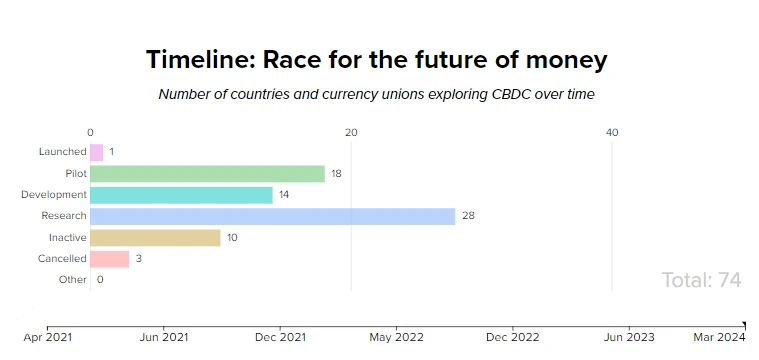
April 2021 state of CBDC in the world
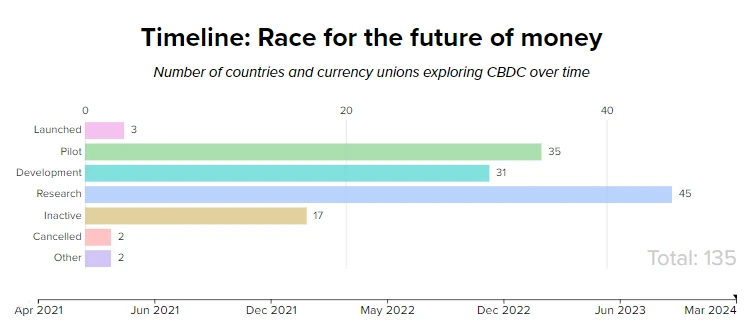
May 2024 state of CBDC in the world
Over the past 3 years, the number of projects being worked on has increased by almost 100%.
We currently have 135 projects.
Three of them have already been enabled in countries such as Nigeria, Jamaica and the Bahamas.
There is dynamic growth in the areas of research, development and piloting.
To take a closer look at the state of CBDC in the world, I recommend two websites: atlanticcouncil and cbdctracker.
Conclusion
Indeed, CBDC represents a significant shift in the global financial landscape.
Surely, it combines the benefits of digital currencies with the stability and regulatory oversight of central banks.
While challenges and risks exist, the potential benefits of CBDC are undeniable.
As countries continue to explore and experiment with CBDC, then it is crucial to strike the right balance between innovation, regulation, and inclusivity.
For society and individuals, CBDC carries many dangers, without doubt.
One of them is restriction of freedom rights, censorship or lack of privacy, but…
Moreover, CBDCs are created not to make life easier for society, but to gain more power for financial institutions.

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.